Understanding the Crn3/16 Heat Sink

The Crn3/16 heat sink is a vital component in electronics, designed to dissipate excess heat generated by various electronic devices. With its efficient heat management capabilities, this heat sink plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance and preventing potential damage to sensitive components. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of Crn3/16 heat sinks, exploring their construction, applications, and the benefits they offer.
Construction and Design
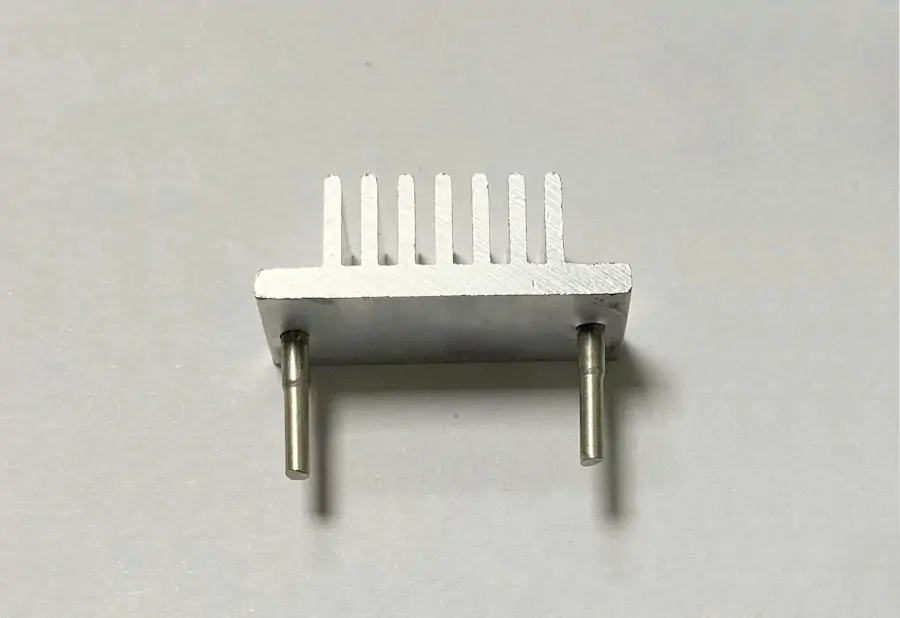
The Crn3/16 heat sink boasts a robust construction, crafted from high-quality aluminum or copper materials. These materials are known for their excellent thermal conductivity, ensuring efficient heat transfer from the heat source to the heat sink. The heat sink features a fin-based design, consisting of multiple thin fins arranged in a specific pattern. This design maximizes the surface area, allowing for effective heat dissipation into the surrounding environment.
Key Features:

- Fin Design: The fin-based structure enhances heat dissipation by providing a larger surface area for heat exchange.
- Material Quality: Aluminum and copper materials offer superior thermal conductivity, ensuring efficient heat transfer.
- Compact Size: Despite its efficient design, the Crn3/16 heat sink maintains a compact size, making it suitable for various applications.
Applications and Benefits

The Crn3/16 heat sink finds widespread use in a range of electronic devices and systems, making it a versatile and essential component. Here are some key applications and benefits:
Electronic Devices:
- Computers: Crn3/16 heat sinks are commonly used in computers to cool central processing units (CPUs) and graphics processing units (GPUs), ensuring stable performance and preventing overheating.
- Laptops: Laptops often utilize these heat sinks to manage heat generated by their compact components, maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
- Power Supplies: Heat sinks are employed in power supplies to dissipate heat from transformers and other heat-generating components, enhancing efficiency and reliability.
Industrial Applications:
- Manufacturing Equipment: In industrial settings, Crn3/16 heat sinks play a crucial role in cooling high-performance machinery and equipment, ensuring smooth operation and preventing equipment failure.
- Telecommunications: Heat sinks are utilized in telecommunications infrastructure to manage heat generated by network equipment, maintaining optimal signal transmission.
- LED Lighting: LED lights often incorporate heat sinks to dissipate heat, extending the lifespan of the LEDs and ensuring consistent lighting performance.
Advantages of Crn3/16 Heat Sinks:
- Efficient Heat Dissipation: The fin-based design maximizes surface area, allowing for effective heat transfer and rapid cooling.
- Compact and Lightweight: Despite their efficient performance, Crn3/16 heat sinks maintain a compact and lightweight design, making them easy to integrate into various devices.
- Versatility: These heat sinks can be adapted to suit different heat-generating components, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Cost-Effective: With their efficient design and affordable price, Crn3/16 heat sinks offer excellent value for money, providing reliable heat management without breaking the bank.
Installation and Maintenance

Installing a Crn3/16 heat sink is a straightforward process, typically involving the following steps:
- Prepare the Surface: Clean the heat-generating component and ensure it is free from any debris or residue.
- Apply Thermal Compound: Apply a thin layer of thermal compound to the surface of the component, ensuring even coverage.
- Attach the Heat Sink: Secure the heat sink onto the component, ensuring a tight and secure fit.
- Connect to Cooling System: If applicable, connect the heat sink to a cooling system, such as a fan or water-cooling setup.
Maintenance Tips:

- Regular Cleaning: Periodically clean the heat sink to remove dust and debris, ensuring optimal heat dissipation.
- Thermal Compound Replacement: Replace the thermal compound every 1-2 years to maintain efficient heat transfer.
- Monitor Temperatures: Keep an eye on the temperatures of the heat-generating component to ensure the heat sink is functioning effectively.
Table: Comparison of Crn3/16 Heat Sinks

| Feature | Crn3/16 Heat Sink |
|---|---|
| Material | Aluminum/Copper |
| Fin Design | Fin-based |
| Size | Compact |
| Thermal Conductivity | High |
| Applications | Electronic Devices, Industrial Equipment |

Notes:
- When installing the heat sink, ensure a firm and even pressure to avoid any air gaps that may affect heat transfer.
- Regularly check the thermal compound for any signs of drying or cracking, as this can impact heat dissipation.
- For optimal performance, consider using a high-quality thermal compound specifically designed for heat sinks.
Conclusion:

The Crn3/16 heat sink stands out as a reliable and efficient solution for managing excess heat in electronic devices and industrial applications. With its compact design, high thermal conductivity, and versatile applications, it plays a crucial role in maintaining the performance and longevity of various components. By understanding the construction, features, and benefits of the Crn3/16 heat sink, you can make informed decisions when selecting the right heat management solution for your specific needs.
FAQ:

What is the primary function of a heat sink?
+
A heat sink’s primary function is to dissipate excess heat generated by electronic components, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance.
Can I use a Crn3/16 heat sink for my custom-built PC?

+
Absolutely! Crn3/16 heat sinks are commonly used in custom PC builds to cool CPUs and GPUs, providing efficient heat management for stable performance.
How often should I replace the thermal compound on my heat sink?

+
It is recommended to replace the thermal compound every 1-2 years to maintain optimal heat transfer. Regularly inspect the compound for any signs of deterioration.
Are there any alternative materials for heat sinks besides aluminum and copper?
+Yes, heat sinks can also be made from materials like ceramic and graphite, each offering unique thermal properties and applications.